When it comes to motorcycles, there are various components and parts that contribute to their functionality. One crucial element that often goes unnoticed but plays a vital role in a motorcycle’s electrical system is the stator. In this comprehensive article, we will delve deep into the world of motorcycle stators, understanding their significance, how they work, and why they are essential for every bike enthusiast. So, let’s kickstart our journey by exploring the basics.
Understanding the Stator
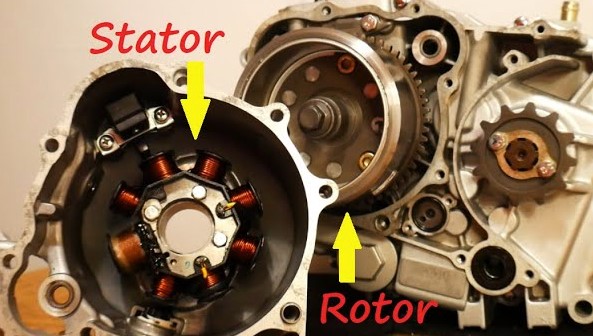
What Exactly Is a Stator?
A stator is a fundamental component in a motorcycle’s electrical system. It is essentially a stationary part of the alternator, responsible for generating electricity to power the motorcycle’s electrical components. While the stator may not be as prominent as the engine or the wheels, it plays a pivotal role in ensuring that your motorcycle operates smoothly.
The Anatomy of a Stator
Before we dive deeper, let’s break down the anatomy of a stator. A typical stator consists of copper wire windings, a core, and a cover. These components work in harmony to produce electrical energy. The copper wire windings are wound around the core, creating a magnetic field when electricity flows through them. This magnetic field is crucial for generating electrical power.
Stator Location
Stators are typically located on the left side of the motorcycle engine, near the flywheel. This strategic placement allows them to work efficiently with other components of the electrical system.
How Does a Stator Work?
Understanding the inner workings of a stator is essential to comprehend its role in a motorcycle. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how a stator generates electricity:
- Rotation of the Engine: When you start your motorcycle, the engine begins to rotate.
- Movement of the Magnets: Inside the engine, there are magnets attached to the flywheel. As the engine spins, these magnets also rotate.
- Generating Alternating Current (AC): The rotating magnets create a magnetic field that passes through the stator’s copper wire windings. This interaction induces an alternating current (AC) in the copper coils.
- Conversion to Direct Current (DC): While motorcycles require direct current (DC) to power their electrical components, the AC generated by the stator needs to be converted. This is where the rectifier comes into play. It converts the AC into DC, making it suitable for the motorcycle’s electrical system.
- Powering the Electrical Components: The DC electricity produced by the stator is then used to power various components, such as the lights, ignition system, and battery charging system.
The Significance of a Healthy Stator
Maintaining a healthy stator is crucial for the overall performance of your motorcycle. Here are some reasons why:
Smooth Engine Operation
A functioning stator ensures that your motorcycle’s engine runs smoothly. It provides the necessary electrical power to keep the engine running, allowing you to enjoy a hassle-free ride.
Charging the Battery
The stator plays a pivotal role in charging the motorcycle’s battery. A well-charged battery is essential for starting the bike and powering its electrical components.
Illumination
The lights on your motorcycle, including the headlights, taillights, and turn signals, rely on the stator’s electrical output. A malfunctioning stator can lead to dim or non-functional lights, compromising your safety on the road.
Ignition System
The stator also powers the ignition system, ensuring that your motorcycle starts without any issues. A faulty stator can result in starting problems and engine misfires.
Signs of a Failing Stator
Like all motorcycle components, stators can also wear out or fail over time. It’s essential to be aware of the signs of a failing stator:
- Dimming Lights: If you notice your motorcycle’s lights becoming dimmer, it could be a sign of a failing stator.
- Battery Issues: Difficulty starting your bike or repeated dead batteries may indicate a stator problem.
- Electrical Component Failures: Malfunctions in various electrical components, such as the horn or turn signals, can be attributed to a failing stator.
- Engine Stalling: A failing stator can lead to engine stalling, making your motorcycle unreliable.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the stator is a crucial component in a motorcycle’s electrical system. It generates the electrical power necessary to keep your bike running smoothly, charge the battery, and power various electrical components. Understanding its importance and keeping an eye out for signs of failure can help you maintain your motorcycle’s performance and safety.